News & Insights
Smart Manufacturing: shaping the future of food and beverage
The food and beverage manufacturing sector is rapidly transforming with the help of technology and automation. This adoption is boosting efficiency, quality, and safety, benefiting both consumers and manufacturers. Salas O’Brien shares the latest trends in technology and automation, including digital twins, tracking and tracing, robotics and automation, artificial intelligence/machine learning.
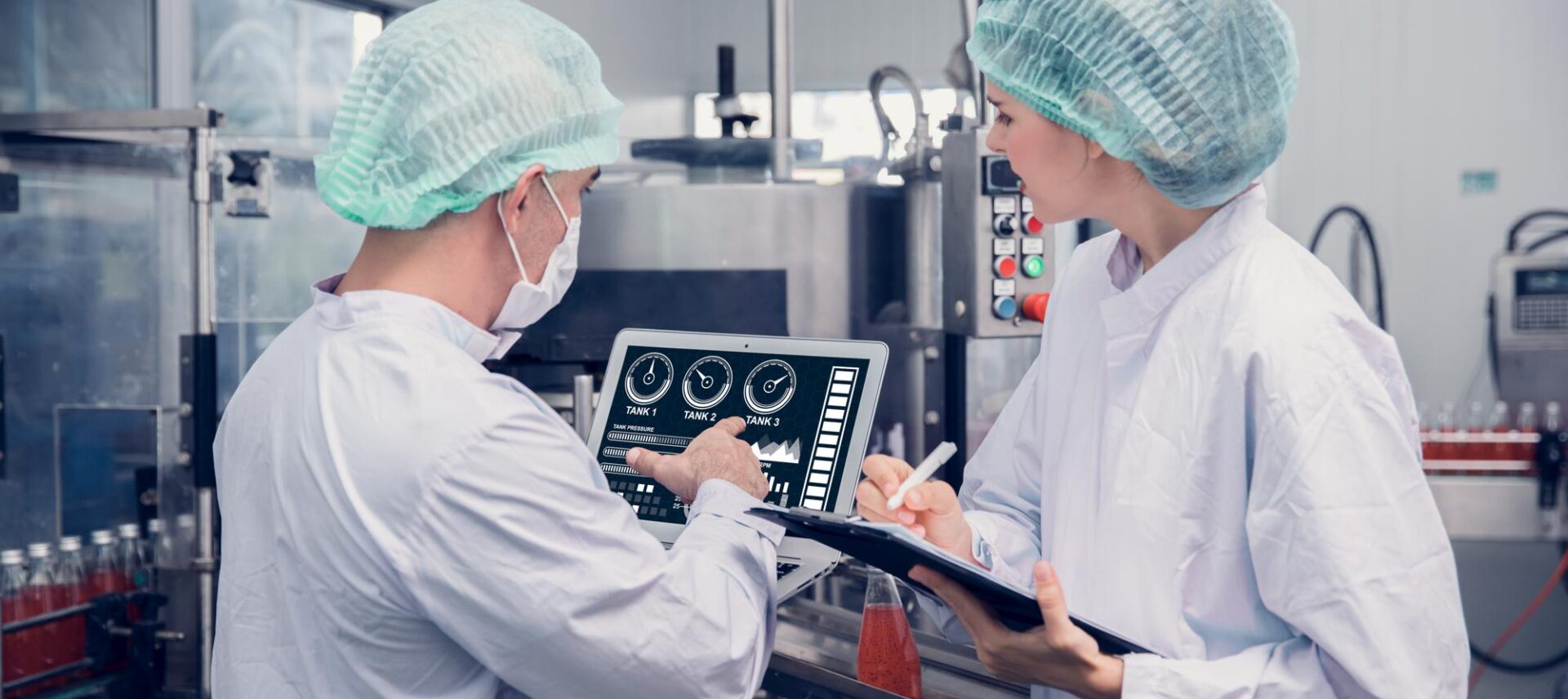

The food and beverage manufacturing sector is advancing into the digital age. In recent years, there has been a significant shift towards technology and automation, leading to the creation of smart factories and sparking conversation about digital transformation. The promise is a new phase of heightened efficiency, improved quality, and increased safety in the industry, bringing benefits to consumers, manufacturers, and communities.
However, the key question from our clients is about implementation. It’s one aspect to acknowledge the introduction of new technologies, but a different challenge to effectively utilize them.
This article delves into the cutting-edge trends fueling modern smart factories and provides practical insights on making them productive. From the implementation of robotics, data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning, to the adoption of digital twins, and thorough track and trace systems, the opportunity to progressively overhaul the production of food and beverages is real and attainable.
What’s driving the digital transformation in food and beverage manufacturing?
One major force propelling digital transformation in food and beverage manufacturing is the need for efficiency and increased productivity.
Food and beverage manufacturers are continuously seeking ways to optimize their operations, reduce costs, and increase their OEE and output. Integrating advanced technologies such as AI, machine learning, and robotics can help achieve these goals. For instance, AI and machine learning algorithms can analyze large amounts of data quickly and accurately, leading to better decision-making in real time. On the other hand, robotics can handle repetitive tasks more efficiently than humans, freeing up the human workforce to focus on more complex, creative tasks.
Moreover, the growing global emphasis on sustainability is pushing companies to reevaluate their processes and explore more environmentally friendly options.
This is where technology certainly comes into play. Merging the best of both worlds—human creativity and technological ability—provides an opportunity for businesses to become more sustainable. For example, AI and machine learning can be used to create more efficient supply chains that reduce waste. Meanwhile, humans can use their problem-solving skills and creativity to devise innovative solutions for reducing their company’s environmental footprint. In essence, the shift towards smart factories is not just a technological evolution, but also a cultural and environmental one.
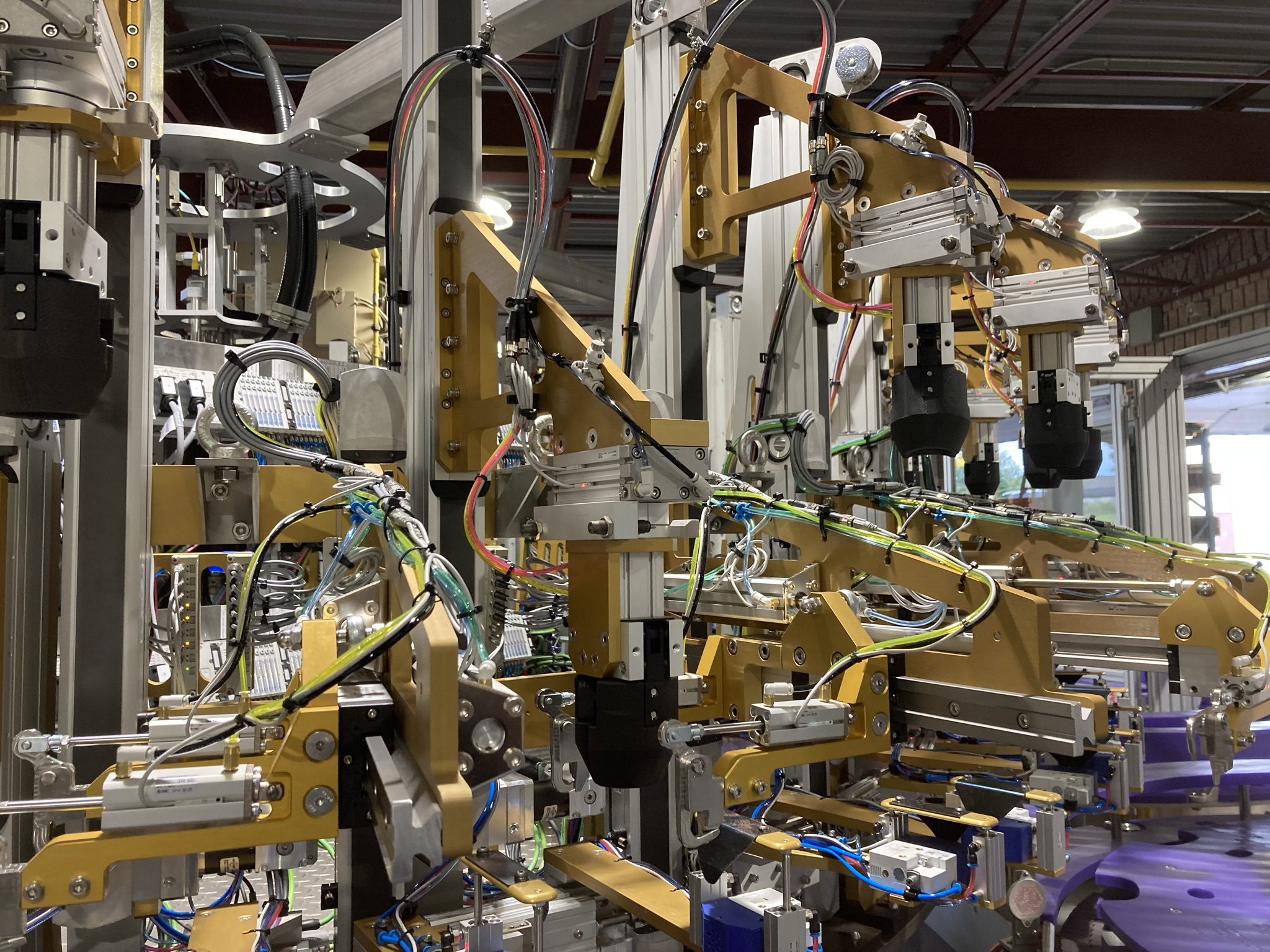

Robotics and automation: streamlining production processes
Automation isn’t new. It has become a cornerstone of modern food and beverage manufacturing facilities. From robotic arms that precisely handle delicate ingredients to automated assembly lines, these technologies can perform repetitive tasks with precision and speed, minimizing the risk of human error and ensuring product uniformity.
A central theme is the concept of “cobots”, or collaborative robotics, where humans and machines work together, maximizing the strengths of both. While machines excel at tasks that require precision, speed, and consistency, humans bring unique abilities such as creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence to the table.
Plant managers are increasingly turning to digital solutions because they understand that tasks like packing boxes for an entire shift can lead to employee burnout. By automating these mundane, repetitive tasks, workers can be redirected to more fulfilling and impactful roles. This creates a more rewarding work environment where employees can contribute meaningfully, stimulating their intellectual capacities rather than exhausting their physical stamina.
Moreover, automation can empower factories with the flexibility to pivot their production lines swiftly. This is especially crucial in a fast-paced, dynamic market where consumer demands and trends are continuously evolving. With automation, factories can switch from manufacturing one product to another with minimal downtime, optimizing productivity and responding more effectively to market changes.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning: driving innovation
Artificial intelligence and machine learning have emerged as powerful tools in food and beverage manufacturing. These technologies enable advanced data analysis, predictive modeling, and intelligent decision-making. AI-powered systems can optimize production parameters, forecast demand, and streamline inventory management. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to detect patterns and anomalies, aiding in quality assurance and predictive maintenance.
AI can also deliver a personalized customer experience. Increasingly AI is enabling more effective marketing strategies by allowing companies to segment their consumer base and tailor their advertising content based on individual preferences. For example, AI algorithms can analyze a consumer’s past purchases, dietary preferences, and even social media activity to provide personalized product recommendations ranging from suggesting a new craft beer brand for a beer enthusiast or a brand of gluten-free pasta for someone with gluten-sensitivity.
Implementing artificial intelligence and machine learning works best in a phased approach. This allows for the benefits to be seen as each successive phase is reached. Measuring wins with a phase-by-phase approach provides the evidence needed to create buy-in from even the skeptical on a team.
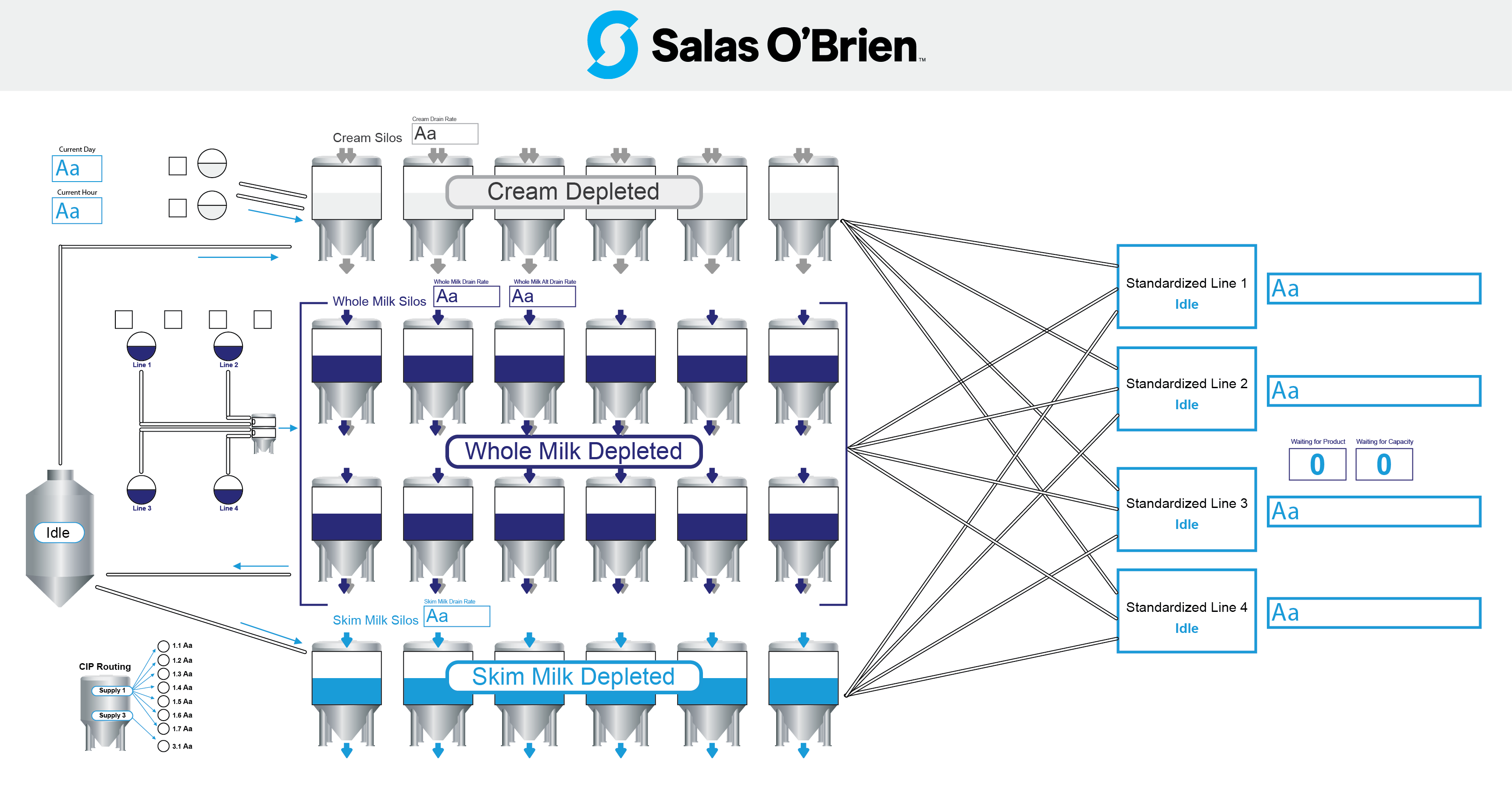
Digital twins: enhancing operations and optimization
One of the cutting-edge technologies revolutionizing food and beverage manufacturing is digital twin technology. Digital twins offer real-time digital replicas that allow manufacturers to visualize, predict, and optimize plant operations with reduced risk and improved reliability. By leveraging IoT sensors, data analytics, and machine learning algorithms, digital twins provide a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing environment, enabling proactive problem-solving and continuous improvement.
A true digital twin at its most basic level facilitates decision-making by leveraging hindsight and foresight. Most factories rely on the knowledge of someone who has been there for many years—the person who embodies the history of the plant. But those people are retiring and often, the next generation isn’t following the same career path. Digital twins are the technological answer to this.
By analyzing data and machine performance over time, digital twins allow companies to predict when parts need replacing before they fail altogether so that measures can be taken early enough to avoid serious upsets down the line. They provide valuable information on decisions like whether investments should be made into new machinery versus retrofitting existing infrastructure. They remember the workflows that failed and the ones that succeeded.
Implementing digital twin technology requires a commitment to bringing all the pertinent information into a single source of truth. Once those disparate data sources are connected, better control and more insightful actions are possible when contextualized together, leading to holistic smart manufacturing.
Digital track and trace: ensuring transparency and safety
Consumer demand for transparency and product safety has never been higher, and the risk of public opinion going viral through social media is real. Technology is playing a crucial role in meeting these expectations and mitigating risk through robust tracking and tracing systems.
By leveraging enhanced data aggregation, barcode scanning, RFID tags, and blockchain technology, manufacturers can effectively monitor and trace products, 100% digitally, throughout the supply chain. This level of transparency enhances quality control, improves recall management, enhances flexibility of manufacturing, and enables swift response in case of contamination or safety concerns.
One thing the global Covid-19 pandemic taught manufacturers was that the supply chain wasn’t as robust as they hoped. It wound up accelerating implementation of digital tracking and tracing technology to create better connections and more efficient movement of products. This implementation also helped enhance quality control and safety of the food supply.
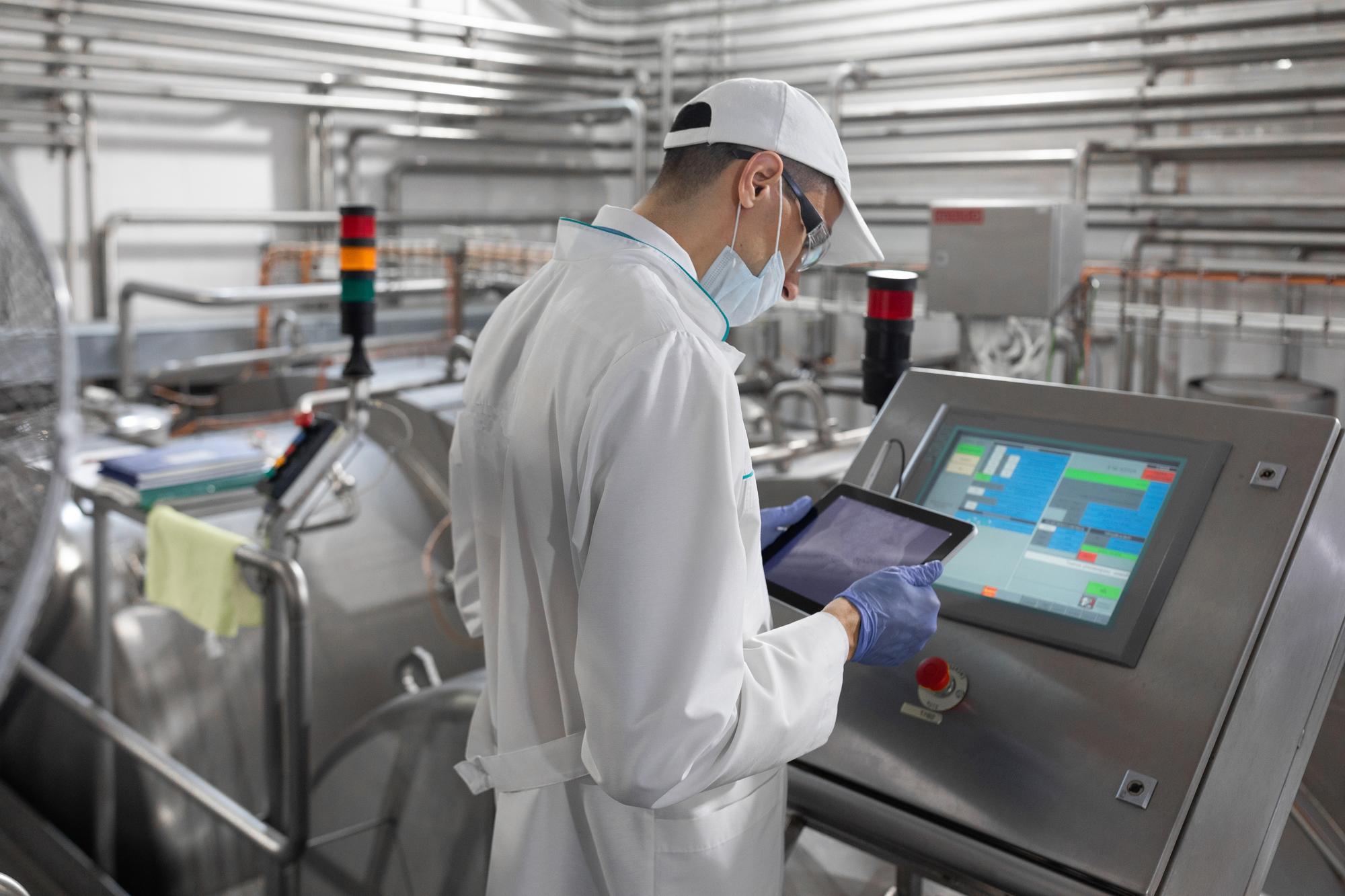

Implementing practical solutions to deliver smart manufacturing
Salas O’Brien is a leader in food and beverage manufacturing and a leader in the delivery of smart manufacturing solutions and technology.
We work with clients daily on the practical implementation of technology that enhances efficiency, quality, and sustainability, paving the way for a more promising future in the realm of food and beverage manufacturing.
Want to talk about how this might impact your operations? We would love to connect with you. Simply contact us.
For media inquiries on this article, reach out to Stacy Lake.
Sustainability in F&B Manufacturing

John Glenski, CPM
John Glenski is a leader in digital transformation in the industrial sector with a demonstrated history of providing data-driven outcomes for the world’s largest manufacturers. John works collaboratively with internal and external partners to deliver innovative solutions for smart manufacturing (automation, material handling, and data/information solutions) with a focus on sustainable applications. John serves as a Principal & Senior Director of Automation & Digital at Salas O’Brien. Contact him at [email protected].

